4 Packing Files onto Disks
Problem Specification
Suppose, you want to copy a set of files from your hard-disk onto as few as possible diskettes of a given size, e. g. onto common 1.44 MB diskettes. In case your files do not fit on a single diskette, it might become quite tricky to figure out the minimal number of needed diskettes and how to partition the files.
Model
A diskette is modeled by a set  . All sets
. All sets  form a partition of the set of all files
form a partition of the set of all files 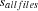 , i. e., all
, i. e., all  are pairwise disjoint and their union is
are pairwise disjoint and their union is 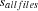 . The sizes of all files contained in a set is summed up and compared with the fixed capacity of the diskette.
. The sizes of all files contained in a set is summed up and compared with the fixed capacity of the diskette.
Distribution Strategy
The distribution is two-dimensional.
Distribute the number of diskettes starting from the minimal number possible. The minimal number is the ceiling of dividing the sum of all file sizes by the diskette size.
Distribute the files over the sets representing the individual diskettes.
The distribution over the files could be refined by taking the size of the actual file into account. This is subject to experimentation by the reader.
Solver
The function SpreadFiles returns a solver configured according to the actual values of the formal arguments Files and DiskCap. The returned solver's root variable Disks contains the set of diskettes of size DiskCap needed to store all files in Files and specifies what files have to be stored on which diskette.
The argument Files holds a list of individual files, where each file is represented by a record with label file and the features name and size. The argument DiskCap is an integer. The variable FileSizes holds a list of all files sizes and Size stores the sum all elements in FileSizes. The lower bound of the number of diskettes is held in LB. The finite domain NbDisks is used to distribute over the number of diskettes. Each file in Files is represented by an integer in ascending order starting from 1. These integers are stored in AllFiles. Finally, the sets representing the individual diskettes are held in Ds.
First, the number of diskettes is distributed starting from LB. Then, Ds is initialized to sets containing maximal all files. Next, the constraint that all elements of Ds are a partition of the set of all files is imposed. Finally, the maximum capacity of all diskettes is limited to DiskCap by imposing for all elements of Ds the constraint that the sum of the size of all their elements is less or equal to DiskCap. The implementation uses FS.reified.areIn to associate the containment of individual elements of sets to 0/1 variables. These 0/1 variable are passed to FD.sumC to ensure that a diskettes capacity is not exceeded. Distribution over Ds tries to locate file onto diskettes.
Particularities
The solver represents internally individual file as integers since finite set constraints in Oz can only deal with non-negative integers. To make the produced solution readable to humans, a diskette is represented as record where the features are the files to be stored on that diskette. Such a record is constructed by imposing a feature constraint onto each element of Disks. Then the actual features representing the filenames are added successively by mapping the elements of the set representing the diskettes to their names. Every feature refers to the size of the file it represents. Finally, the feature constraint becomes a record by constraining its arity's width to the number of features.
declare
fun {SpreadFiles Files DiskCap}
proc {$ Disks}
FileSizes = {Map Files fun {$ F} F.size end}
Size = {FoldL FileSizes Number.'+' 0}
LB = Size div DiskCap +
if Size mod DiskCap==0 then 0 else 1 end
NbDisks = {FD.int LB#FD.sup}
AllFiles = {List.number 1 {Length Files} 1}
Ds
in
{FD.distribute naive [NbDisks]}
{FS.var.list.upperBound NbDisks AllFiles Ds}
{FS.partition Ds {FS.value.make AllFiles}}
{ForAll Ds proc {$ D} BL in
{FS.reified.areIn AllFiles D BL}
{FD.sumC FileSizes BL '=<:' DiskCap}
end}
{FS.distribute naive Ds}
Disks = {Map Ds
fun {$ D}
Disk = {RecordC.tell diskette}
in
{ForAll {FS.monitorIn D}
proc {$ E}
F = {Nth Files E}
in
Disk^(F.name) = F.size
end}
{RecordC.width Disk} = {FS.card D}
Disk
end}
end
end
Invoking the solver by
declare Disks =
{SearchOne {SpreadFiles [file(name:a size:360)
file(name:b size:850)
file(name:c size:630)
file(name:d size:70)
file(name:e size:700)
file(name:f size:210)]
1440}}produces the following result:
[[diskette(a:360 b:850 f:210) diskette(c:630 d:70 e:700)]] The input data for this solver can be easily obtained from the respective operating system by using the module OS (see Chapter 21 of ``System Modules'' for details].