7.2 Canvas widget
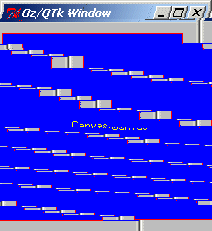
local C Desc=canvas(handle:C width:200 height:200)in {{QTk.build td(Desc)} show} {C create(rect 10 10 190 190 fill:blue outline:red)} {C create(text 100 100 text:"Canvas" fill:yellow)}end
7.2.1 Description
Canvas widgets implement structured graphics. A canvas displays any number of items, which may be things like rectangles, circles, lines, and text. Items may be manipulated (e.g. moved or re-colored) and commands may be associated with items in much the same way that the bind command allows commands to be bound to widgets. This means that items in a canvas can have behaviors defined by the Oz commands bound to them.
Normally the origin of the canvas coordinate system is at the upper-left corner of the window containing the canvas. It is possible to adjust the origin of the canvas coordinate system relative to the origin of the window using the xview and yview widget commands; this is typically used for scrolling. Canvases do not support scaling or rotation of the canvas coordinate system relative to the window coordinate system. The coordinates can be specified either as floats or integers, but they are returned as floats only.
Individual items may be moved or scaled using widget commands described below, but they may not be rotated.
7.2.2 Parameter List
Specific Parameters
closeenoughconfineheightscrollregionwidthxscrollincrementyscrollincrement
Non Specific Parameters
backgroundborderwidthcursorfeaturegluehandlehighlightbackgroundhighlightcolorhighlightthicknessinsertbackgroundinsertborderwidthinsertofftimeinsertontimeinsertwidthlooklrscrollbaronCreationpadxpadyreliefscrollwidthselectbackgroundselectborderwidthselectforegroundtakefocustdscrollbartooltips
7.2.3 Method List
'raise'
'raise'(1:W): If the W argument is omitted then the command raises the widget so that it is above all of its siblings inthe stacking order (it will not be obscured by any siblings and will obscure any siblings that overlap it). IfW is specified then it must be a handle to another widget that is either a sibling of this widget or thedescendant of a sibling of this widget. In this case the 'raise' command will insert this widget into the stacking orderjust above W; this could end up either raisingor lowering the widget.
bind
bind(event:E action:A args:LA append:AP): Specifies an action LA to execute when the event E is triggered.
Actions can be specified either as a procedure, a pair
Port#Messageor a pairObject#Method(see Section 4.3.3).Events are strings (see Section 8.11.1).
The list of arguments
LAspecifies supplementary information to pass to the action, like the key code of a keypress, or the mouse coordinates of a mouse button click (see Section 8.11.2). IfLAif not specified,nilis assumed.The boolean
appendparameter specifies if the binding overrides the previous binding for this event, or adds a supplementary action. If not specified,falseis assumed.
canvasx
canvasx(1:I 2:V: or canvasx(1:I 2:I 3:V): Returns the canvas x-coordinate corresponding to a window coordinate. The first parameter specifies the window coordinate. This method binds the last parameter to the corresponding canvas coordinate. If a supplementary second parameter is given, then the canvas coordinate is rounded to the nearest multiple of that parameter.
canvasy
canvasy(1:I 2:V: or canvasy(1:I 2:I 3:V): Returns the canvas y-coordinate corresponding to a window coordinate. The first parameter specifies the window coordinate. This method binds the last parameter to the corresponding canvas coordinate. If a supplementary second parameter is given, then the canvas coordinate is rounded to the nearest multiple of that parameter.
create
create(1:A ...): Creates a new item in the canvas of type A. The exact format of the arguments after type depends on type, but usually they consist of the coordinates for one or more points, followed by specifications for zero or more item options. If a handle parameter is specified, it is bound to an Oz object controlling the canvas item. See the subsections on individual item types below for more on the syntax of this command.
focus
focus(1:R): Set the keyboard focus for the canvas widget to the item given by R. If R refers to several items, then the focus is set to the first such item in the display list that supports the insertion cursor. If R doesn't refer to any items, or if none of them support the insertion cursor, then the focus isn't changed. If R is an empty string, then the focus item is reset so that no item has the focus.
get
get(parameter1:Variable1 ... parameterX:VariableX): Obtains the value of one or more parameters. parameterX must be a valid parameter for the widget. VariableX must be free variables that will receive the current value of the parameters.
getFocus
getFocus(force:B): if B is false (or by default): if the application currently has the input focus on the widget's display, this command resets the input focus for the widget's display to the widget. If the application doesn't currently have the input focus on the widget's display, the widget will be remembered as the focus for its top-level; the next time the focus arrives at the top-level, it will be redirected it to the widget. If B is true: sets the focus of the widget's display to the widget, even if the application doesn't currently have the input focus for the display. This command should be used sparingly, if at all. In normal usage, an application should not claim the focus for itself; instead, it should wait for the window manager to give it the focus. B must be a boolean.
getGrabStatus
getGrabStatus(1:V): Binds V to the atom none if there is no grab on the widget, to the atom local if there is a local grab and to global if there is a global grab. V must be a free variable.
lower
lower(1:W): If the W argument is omitted then the command lowers the widget so that it is below all of its siblings inthe stacking order (it will be obscured by any siblings and will not obscure any siblings that overlap it). IfW is specified then it must be a handle to another widget that is either a sibling of this widget or thedescendant of a sibling of this widget. In this case the lower command will insert this widget into the stacking orderjust below W; this could end up either raisingor lowering the widget.
newTag
newTag(1:V): Binds V to a canvas tag (see Section 7.2.5 for details).
postscript
postscript(param1:value1 ... paramX:valueX: Generate a Postscript representation for part or all of the canvas. The Postscript is created in Encapsulated Postscript form using version 3.0 of the Document Structuring Conventions. Note: by default Postscript is only generated for information that appears in the canvas's window on the screen. If the canvas is freshly created it may still have its initial size of 1x1 pixel so nothing will appear in the Postscript. To get around this problem either invoke the update command to wait for the canvas window to reach its final size, or else use the width and height options to specify the area of the canvas to print. The option-value argument pairs provide additional information to control the generation of Postscript. The following options are supported:
colormode:A: Specifies how to output color information.Amust becolor(for full color output),gray(convert all colors to their gray-scale equivalents) ormono(convert all colors to black or white).file:VS: Specifies the name of the file in which to write the Postscript.VSmust be a virtual string.height:P: Specifies the height of the area of the canvas to print. Defaults to the height of the canvas window.Pmust be a valid distance (see Section 8.6).pageanchor:A: Specifies which point of the printed area of the canvas should appear over the positioning point on the page (which is given by thepagexandpageyoptions). For example,pageanchor:nmeans that the top center of the area of the canvas being printed (as it appears in the canvas window) should be over the positioning point. Defaults tocenter.Amust be one the following atoms:n,s,e,w,nw,ne,sw,seorcenter.pageheight:P: Specifies that the Postscript should be scaled in both x and y so that the printed area isPhigh on the Postscript page. Defaults to the height of the printed area on the screen. If bothpageheightandpagewidthare specified then the scale factor frompagewidthis used (non-uniform scaling is not implemented).Pmust be a valid distance (see Section 8.6).pagewidth:P: Specifies that the Postscript should be scaled in both x and y so that the printed area isPwide on the Postscript page. Defaults to the width of the printed area on the screen. If bothpageheightandpagewidthare specified then the scale factor frompagewidthis used (non-uniform scaling is not implemented).Pmust be a valid distance (see Section 8.6).pagex:P:Pgives the x-coordinate of the positioning point on the Postscript page. Used in conjunction with thepageyandpageanchoroptions to determine where the printed area appears on the Postscript page. Defaults to the center of the page.Pmust be a valid distance (see Section 8.6).pagey:P:Pgives the y-coordinate of the positioning point on the Postscript page. Used in conjunction with thepagexandpageanchoroptions to determine where the printed area appears on the Postscript page. Defaults to the center of the page.Pmust be a valid distance (see Section 8.6).rotate:B: Specifies whether the printed area is to be rotated 90 degrees. In non-rotated output the x-axis of the printed area runs along the short dimension of the page (``portrait'' orientation); in rotated output the x-axis runs along the long dimension of the page (``landscape'' orientation). Defaults to non-rotated.Bmust be a boolean.width:P: Specifies the width of the area of the canvas to print. Defaults to the width of the canvas window.Pmust be a valid distance (see Section 8.6).x:P: Specifies the x-coordinate of the left edge of the area of the canvas that is to be printed, in canvas coordinates, not window coordinates. Defaults to the coordinate of the left edge of the window.Pmust be a valid distance (see Section 8.6).y:P: Specifies the y-coordinate of the top edge of the area of the canvas that is to be printed, in canvas coordinates, not window coordinates. Defaults to the coordinate of the top edge of the window.Pmust be a valid distance (see Section 8.6).
releaseGrab
releaseGrab: Releases the grab on the widget if there is one, otherwise does nothing.
scan
scan(...): This command is used to implement scanning on canvases. It has two forms, depending on option:
scan(mark X Y): Records x and y and the canvas's current view; used in conjunction with laterscan(dragto ...)commands. Typically this command is associated with a mouse button press in the widget andXandYare the coordinates of the mouse.XandYmust be valid distances (see Section 8.6).scan(dragto X Y): This command computes the difference between itsXandYarguments (which are typically mouse coordinates) and theXandYarguments to the lastscan(mark ...)command for the widget. It then adjusts the view by 10 times the difference in coordinates. This command is typically associated with mouse motion events in the widget, to produce the effect of dragging the canvas at high speed through its window.
select
select(...): Manipulates the selection in one of several ways, depending on option. The command may take any of the forms described below. In all of the descriptions below, Tag must refer to an item that supports indexing and selection; if it refers to multiple items then the first of these that supports indexing and the selection is used.
select(adjust Tag I): Locate the end of the selection inTagnearest to the character given byI, and adjust that end of the selection to be atI(i.e. including but not going beyondI). The other end of the selection is made the anchor point for future select to commands. If the selection isn't currently inIthen this command behaves the same as theselect(to ...)widget command.select(clear): Clear the selection if it is in this widget. If the selection isn't in this widget then the command has no effect.select(from Tag I): Set the selection anchor point for the widget to be just before the character given byIin the item given byTag. This command doesn't change the selection; it just sets the fixed end of the selection for futureselect(to ...)commands.select(to Tag I): Set the selection to consist of those characters ofTagbetween the selection anchor point andI. The new selection will include the character given byI; it will include the character given by the anchor point only if index is greater than or equal to the anchor point. The anchor point is determined by the most recentselect(adjust ...)orselect(from ...)command for this widget. If the selection anchor point for the widget isn't currently inTag, then it is set to the same character given byI.
set
set(parameter1:value1 ... parameterX:valueX): Changes the value of one or more parameters. parameterX must be a valid parameter for the widget. valueX must be a valid value for the parameter.
setGrab
setGrab(global:B): Sets a grab on the widget. If B is true then the grab is global, otherwise it is local (B false by default). If a grab was already in effect for this application then it is automatically released. If there is already a grab on the widget and it has the same global/local form as the requested grab, then the command does nothing. Local grab affects only the grabbing application: events willbe reported to other applications as if the grab had never occurred. A global grablocks out all applications on the screen, so that only the given subtree of the grabbing application will besensitive to pointer events (mouse button presses, mouse button releases, pointer motions, window entries, andwindow exits). During global grabs the window manager will not receive pointer events either. Warning: whe a grab is set, it is define for the whole Oz process so that it will prevent the user to do input to other windows as well. Moreover a grab is still effective even if the window that contains the grabbed widgets is hidden. B must be a boolean.
winfo
winfo(parameter1:value1 ... parameterX:valueX): This commands works like the get method, but for window-related information. For more details, see Section 8.9.
7.2.4 Detailed Parameters List
closeenough
closeenough:F: Specifies a floating-point value indicating how close the mouse cursor must be to an item before it is considered to be ``inside'' the item. Defaults to 1.0. F must be a float value.
confine
confine:B: Specifies a boolean value that indicates whether or not it should be allowable to set the canvas's view outside the region defined by the scrollregion argument. Defaults to true, which means that the view will be constrained within the scroll region. B must be a boolean.
height
height:P: Specifies a desired window height that the canvas widget should request from its geometry manager. P must be a valid screen distance (see Section 8.6).
background
background:C: or bg:C: Specifies the normal background color to use when displaying the widget. C must be a valid color (see Section 8.2).
borderwidth
borderwidth:P: Specifies a non-negative value indicating the width of the 3-D border to draw around the outside of the widget (if such a border is being drawn; the relief option typically determines this). The value may also be used when drawing 3-D effects in the interior of the widget. P must be a valid screen distance (see Section 8.6).
cursor
cursor:A: Specifies the mouse cursor to be used for the widget. A must be a valid cursor (see Section 8.7)
feature
feature:A: Specifies a feature name for the container object to reference the object controlling this widget. For more details, see Section 4.2. A must be an atom.
glue
glue:A: Specifies how a widget must fit in its own available place. A must be an atom that is any combination of n, s, w and e. If a direction is specified, the corresponding border is glued to its neighbor or border of the frame if there is no neighbor. If a direction is not specified, the corresponding border if such that the widget takes just the width or height it needs to draw itself. If none of opposite directions is specified, the widget is centered. For more details, see Section 4.1.
handle
handle:V: Specifies a variable to reference the object controlling this widget. This variable is bound when the window is built. For more details, see Section 4.2. V must be a free variable.
highlightbackground
highlightbackground:C: Specifies the color to display in the traversal highlight region when the widget does not have the input focus. C must be a valid color (see Section 8.2)
highlightcolor
highlightcolor:C: Specifies the color to use for the traversal highlight rectangle that is drawn around the widget when it has the input focus. C must be a valid color (see Section 8.2)
highlightthickness
highlightthickness:P: Specifies a non-negative value indicating the width of the highlight rectangle to draw around the outside of the widget when it has the input focus. If the value is zero, no focus highlight is drawn around the widget. P must be a valid screen distance (see Section 8.6).
insertbackground
insertbackground:C: Specifies the color to use as background in the area covered by the insertion cursor. This color will normally override either the normal background for the widget (or the selection background if the insertion cursor happens to fall in the selection). C must be a valid color (see Section 8.2).
insertborderwidth
insertborderwidth:P: Specifies a non-negative value indicating the width of the 3-D border to draw around the insertion cursor. P must be a valid screen distance (see Section 8.6).
insertofftime
insertofftime:I: Specifies a non-negative integer value indicating the number of milliseconds the insertion cursor should remain "off" in each blink cycle. If this option is zero then the cursor doesn't blink: it is on all the time. I must be a positive integer value.
insertontime
insertontime:I: Specifies a non-negative integer value indicating the number of milliseconds the insertion cursor should remain "on" in each blink cycle. I must be a positive integer value.
insertwidth
insertwidth:P: Specifies a value indicating the total width of the insertion cursor. If a border has been specified for the insertion cursor (using the insertborderwidth option), the border will be drawn inside the width specified by the insertwidth option. P must be a valid screen distance (see Section 8.6).
look
look:L: Specifies a look to use for the widget. A look specifies default values for the parameters of widgets. This parameter can be specified at creation time only. Moreover changing a look will not change the appearance of widgets that are already displayed with that look. See Section 5.1 for more details.
lrscrollbar
lrscrollbar:B: Determines whether the widget has got a horizontal bar below. This option can be specified at creation time only. B must be a boolean.
onCreation
onCreation:P: When a widget is created, for example by QTk.build, this parameter specifies an action to execute right after the widget has been created, but before returning from the build instruction. It is usefull if one needs the handle of the widget to initialize it in ways not permitted by its description record (for example binding the Enter or Leave mouse events).
padx
padx:P: Specifies how much horizontal external padding to leave on each side of the widget. This space is added outside the widget border. P must be a valid screen distance (see Section 8.6)
pady
pady:P: Specifies how much vertical external padding to leave on each side of the widget. This space is added outside the widget border. P must be a valid screen distance (see Section 8.6)
relief
relief:A: Specifies the 3-D effect desired for the widget. Must be one of these atoms: raised, sunken, flat, ridge, solid or groove. The value indicates how the interior of the widget should appear relative to its exterior; for example, raised means the interior of the widget should appear to protrude from the screen, relative to the exterior of the widget.
scrollwidth
scrollwidth:P: Specifies the width of the vertical and horizontal scrollbars. P must be a valid screen distance (see Section 8.6)
selectbackground
selectbackground:C: Specifies the background color to use when displaying selected items. C must be a valid color (see Section 8.2).
selectborderwidth
selectborderwidth:P: pecifies a non-negative value indicating the width of the 3-D border to draw around selected items. P must be a valid screen distance (see Section 8.6).
selectforeground
selectforeground:C: Specifies the foreground color to use when displaying selected items. C must be a valid color (see Section 8.2).
takefocus
takefocus:B: Determines whether the window accepts the focus during keyboard traversal (e.g., Tab and Shift-Tab). Before setting the focus to a window, the traversal mechanims consult the value of the takeFocus option. A value of false means that the widget should be skipped entirely during keyboard traversal. true means that the widget should receive the input focus as long as it is viewable (it and all of its ancestors are mapped). B must be a boolean.
tdscrollbar
tdscrollbar:B: Determines whether the widget has got a vertical bar at the right. This option can be specified at creation time only. B must be a boolean.
tooltips
tooltips:VS: Specifies a tooltip for the widget. A tooltip is a small message that appears when the mouse cursor if left still over the widget for a while. If VS is set to nil, no tooltip will appear at all. VS must be a virtual string.
scrollregion
scrollregion:Q: Specifies four coordinates describing the left, top, right, and bottom coordinates of a rectangular region. This region is used for scrolling purposes and is considered to be the boundary of the information in the canvas. Q must be a record of the form q(X1 Y1 X2 Y2). X1, Y1, X2 and Y2 must be valid screen distances (see Section 8.6).
width
width:P: Specifies a desired window width that the canvas widget should request from its geometry manager. P must be a valid screen distance (see Section 8.6).
xscrollincrement
xscrollincrement:P: Specifies an increment for horizontal scrolling. If the value of this option is greater than zero, the horizontal view in the window will be constrained so that the canvas x coordinate at the left edge of the window is always an even multiple of xscrollincrement; furthermore, the units for scrolling (e.g., the change in view when the left and right arrows of a scrollbar are selected) will also be xscrollincrement. If the value of this option is less than or equal to zero, then horizontal scrolling is unconstrained. P must be a valid screen distance (see Section 8.6).
yscrollincrement
yscrollincrement:P: Specifies an increment for vertical scrolling. If the value of this option is greater than zero, the vertical view in the window will be constrained so that the canvas y coordinate at the top edge of the window is always an even multiple of yscrollincrement; furthermore, the units for scrolling (e.g., the change in view when the top and bottom arrows of a scrollbar are selected) will also be yscrollincrement. If the value of this option is less than or equal to zero, then vertical scrolling is unconstrained. P must be a valid screen distance (see Section 8.6).
7.2.6 Graphical items
The sections below describe the various types of items supported by canvas widgets. Each item type is characterized by two things: first, the form of the create method used to create instances of the type; and second, a set of configuration options for items of that type.
ARC ITEMS
Items of type arc appear on the display as arc-shaped regions. An arc is a section of an oval delimited by two angles (specified by the start and extent options) and displayed in one of several ways (specified by the style option). Arcs are created with widget commands of the following form:
create(arc X1 Y1 X2 Y2 param1:value1 ... paramX:valueX) The arguments X1, Y1, X2, and Y2 give the coordinates of two diagonally opposite corners of a rectangular region enclosing the oval that defines the arc. After the coordinates there may be any number of option-value pairs, each of which sets one of the configuration options for the item. These same option-value pairs may be used in itemconfigure widget commands to change the item's configuration. The following options are supported for arcs:
extent:I: Specifies the size of the angular range occupied by the arc. The arc's range extends for degrees degrees counter-clockwise from the starting angle given by thestartoption. Degrees may be negative. If it is greater than 360 or less than -360, then degrees modulo 360 is used as the extent.Imust be an integer.fill:C: Fill the region of the arc with the colorC.Cmust be a valid color (see Section 8.2) ornilfor a non-filled arc.outline:C:Cspecifies a color to use for drawing the arc's outline.Cmust be a valid color (see Section 8.2) ornilfor no outline.outlinestipple:B: Indicates that the outline for the arc should be drawn with a stipple pattern;Bspecifies the stipple pattern to use or nil for no bitmap.start:I: Specifies the beginning of the angular range occupied by the arc.Iis given in units of degrees measured counter-clockwise from the 3-o'clock position; it may be either positive or negative.stipple:B: Indicates that the arc should be filled in a stipple pattern;Bspecifies the stipple pattern to use. If thefilloption hasn't been specified then this option has no effect. IfBisnilthen filling is done in a solid fashion.style:A: Specifies how to draw the arc. IfAis the atompieslice(the default) then the arc's region is defined by a section of the oval's perimeter plus two line segments, one between the center of the oval and each end of the perimeter section. IfAis the atomchordthen the arc's region is defined by a section of the oval's perimeter plus a single line segment connecting the two end points of the perimeter section. IfAis the atomarcthen the arc's region consists of a section of the perimeter alone. In this last case thefilloption is ignored.tags:Tag: Specifies a tag to apply to the item.width:C: Specifies the width of the outline to be drawn around the arc's region. If theoutlineoption has been specified asnilthen this option has no effect. Wide outlines will be drawn centered on the edges of the arc's region. This option defaults to1.0.Cmust be a valid screen distance (see Section 8.6).
BITMAP ITEMS
Items of type bitmap appear on the display as images with two colors, foreground and background. Bitmaps are created with widget commands of the following form:
create(bitmap X Y param1:value1 ... paramX:valueX) The arguments X and Y specify the coordinates of a point used to position the bitmap on the display (see the anchor option below for more information on how bitmaps are displayed). After the coordinates there may be any number of parameters, each of which sets one of the configuration options for the item. The following options are supported for bitmaps:
anchor:A: Specifies how to position the bitmap relative to the positioning point for the item.Amust be one of the following atoms:center,n,ne,e,se,s,sw,wornw. This option defaults tocenter.background:C: Specifies a color to use for each of the bitmap pixels whose value is 0.Cmust be a valid color (see Section 8.2). If this option isn't specified, or if it is specified asnil, then nothing is displayed where the bitmap pixels are 0; this produces a transparent effect.bitmap:B: Specifies a Tk pre-defined bitmap to display in the item, or a file containing a bitmap description in the standard X11 or X10 format. The exact way in which the bitmap is displayed may be affected by other options such as anchor or justify. Typically, if this option is specified then it overrides other options that specify a textual value to display in the widget; the bitmap option may be reset to an empty string to re-enable a text display. In widgets that support both bitmap and image options, image will usually override bitmap. This parameter can't be get at runtime, however it can be set.Bcan be one of these atoms:error,gray75,gray50,gray25,gray12,hourglass,info,questhead,question,warning, orBcan be a virtual string beginning by@and then containing the name of a bitmap description in the standard X11 or X10 format like"@x11.xbm"for example.foreground:C: Specifies a color to use for each of the bitmap pixels whose value is 1.Cmust be a valid color (see Section 8.2).tags:Tag: Specifies a tag to apply to the item.
IMAGE ITEMS
Items of type image are used to display images on a canvas. Images are created with widget commands of the following form:
create(image X Y param1:value1 ... paramX:valueX) The arguments X and Y specify the coordinates of a point used to position the image on the display (see the anchor option below for more information). After the coordinates there may be any number of parameters, each of which sets one of the configuration options for the item. The following options are supported for images:
anchor:A: Specifies how to position the bitmap relative to the positioning point for the item.Amust be one of the following atoms:center,n,ne,e,se,s,sw,wornw. This option defaults tocenter.image:I: Specifies the image to display in the item.Imust be an image generated by theQTk.newImagecommand (see Section 8.4).tags:Tag: Specifies a tag to apply to the item.
LINE ITEMS
Items of type line appear on the display as one or more connected line segments or curves. Lines are created with widget commands of the following form:
create(line X1 Y1 ... Xn Yn param1:value1 ... paramX:valueX) The arguments X1 through Yn give the coordinates for a series of two or more points that describe a series of connected line segments. After the coordinates there may be any number of parameters, each of which sets one of the configuration options for the item. The following options are supported for lines:
arrow:A: Indicates whether or not arrowheads are to be drawn at one or both ends of the line.Amust have be one of the following atoms:none(for no arrowheads),first(for an arrowhead at the first point of the line),last(for an arrowhead at the last point of the line), orboth(for arrowheads at both ends). This option defaults tonone.arrowshape:S: Specifies how to draw arrowheads. The shape argument must be a record of the formq(I1 I2 I3)withI1,I2andI3integers.I1gives the distance along the line from the neck of the arrowhead to its tip.I2gives the distance along the line from the trailing points of the arrowhead to the tip, andI3gives the distance from the outside edge of the line to the trailing points. If this option isn't specified then a ``reasonable'' shape is taken.capstyle:A: Specifies the ways in which caps are to be drawn at the endpoints of the line.Amust be one of the following atoms:butt,projectingorround. If this option isn't specified then it defaults tobutt. Where arrowheads are drawn the cap style is ignored.fill:C: Specifies a color to use for drawing the line.Cmust be a valid color (see Section 8.2) ornilfor a non-filled arc.joinstyle:A: Specifies the ways in which joints are to be drawn at the vertices of the line.Amust be one of the following atoms:bevel,miterorround. If this option isn't specified then it defaults tomiter. If the line only contains two points then this option is irrelevant.smooth:B: Specifies whether or not the line should be drawn as a curve. If so, the line is rendered as a set of parabolic splines: one spline is drawn for the first and second line segments, one for the second and third, and so on. Straight-line segments can be generated within a curve by duplicating the end-points of the desired line segment.Bmust be a boolean.splinesteps:I: Specifies the degree of smoothness desired for curves: each spline will be approximated withIline segments. This option is ignored unless thesmoothoption is true.Imust be an integer.stipple:B: Indicates that the line should be filled in a stipple pattern;Bspecifies the stipple pattern to use. If thefilloption hasn't been specified then this option has no effect. IfBisnilthen filling is done in a solid fashion.tags:Tag: Specifies a tag to apply to the item.width:I: Specifies the width of the line. Wide lines will be drawn centered on the path specified by the points. If this option isn't specified then it defaults to 1.0.
OVAL ITEMS
Items of type oval appear as circular or oval regions on the display. Each oval may have an outline, a fill, or both. Ovals are created with widget commands of the following form:
create(oval X1 Y1 X2 Y2 param1:value1 ... paramX:valueX) The arguments X1, Y1, X2, and Y2 give the coordinates of two diagonally opposite corners of a rectangular region enclosing the oval. The oval will include the top and left edges of the rectangle not the lower or right edges. If the region is square then the resulting oval is circular; otherwise it is elongated in shape. After the coordinates there may be any number of parameters, each of which sets one of the configuration options for the item. The following parameters are supported for ovals:
fill:C: Specifies a color to fill the area of the oval.Cmust be a valid color (see Section 8.2) ornilfor a non-filled oval.outline:C:Cspecifies a color to use for drawing the oval's outline.Cmust be a valid color (see Section 8.2) ornilfor no outline.stipple:B: Indicates that the oval should be filled in a stipple pattern;Bspecifies the stipple pattern to use. If thefilloption hasn't been specified then this option has no effect. IfBisnilthen filling is done in a solid fashion.tags:Tag: Specifies a tag to apply to the item.width:I: Specifies the width of the outline of the oval. Wide outlines are drawn centered on the oval path defined byX1,Y1,X2, andY2. If this option isn't specified then it defaults to 1.0.
POLYGON ITEMS
Items of type polygon appear as polygonal or curved filled regions on the display. Polygons are created with widget commands of the following form:
create(polygon X1 Y1 ... Xn Yn param1:value1 ... paramX:valueX)The arguments X1 through Yn specify the coordinates for three or more points that define a closed polygon. The first and last points may be the same; whether they are or not, the polygon if drawed as a closed polygon. After the coordinates there may be any number of parameters, each of which sets one of the configuration options for the item. The following parameters are supported for polygons:
fill:C: Specifies a color to fill the area of the polygon.Cmust be a valid color (see Section 8.2) ornilfor a non-filled oval.outline:C:Cspecifies a color to use for drawing the polygon's outline.Cmust be a valid color (see Section 8.2) ornilfor no outline.smooth:B: Specifies whether or not the polygon should be drawn with a curved perimeter. If so, the outline of the polygon becomes a set of parabolic splines, one spline for the first and second line segments, one for the second and third, and so on. Straight-line segments can be generated in a smoothed polygon by duplicating the end-points of the desired line segment.Bmust be a boolean.splinesteps:I: Specifies the degree of smoothness desired for curves: each spline will be approximated withIline segments. This option is ignored unless thesmoothoption istrue.Imust be an integer.stipple:B: Indicates that the polygon should be filled in a stipple pattern;Bspecifies the stipple pattern to use. If thefilloption hasn't been specified then this option has no effect. IfBisnilthen filling is done in a solid fashion.tags:Tag: Specifies a tag to apply to the item.width:I: Specifies the width of the outline of the polygon. Wide outlines are drawn centered on the polygon path defined byX1,Y1,X2, andY2. If this option isn't specified then it defaults to 1.0.
Polygon items are different from other items such as rectangles, ovals and arcs in that interior points are considered to be ``inside'' a polygon even if it is not filled. For most other item types, an interior point is considered to be inside the item only if the item is filled or if it has neither a fill nor an outline. If you would like an unfilled polygon whose interior points are not considered to be inside the polygon, use a line item instead.
RECTANGLE ITEMS
Items of type rectangle appear as rectangular regions on the display. Each rectangle may have an outline, a fill, or both. Rectangles are created with widget commands of the following form:
create(rectangle X1 Y1 X2 Y2 param1:value1 ... paramX:valueX) The arguments X1, Y1, X2, and Y2 give the coordinates of two diagonally opposite corners of the rectangle (the rectangle will include its upper and left edges but not its lower or right edges). After the coordinates there may be any number of parameters for the item. The following parameters are supported for rectangles:
fill:C: Specifies a color to fill the area of the rectangle.Cmust be a valid color (see Section 8.2) ornilfor a non-filled rectangle.outline:C:Cspecifies a color to use for drawing the rectangle's outline.Cmust be a valid color (see Section 8.2) ornilfor no outline.stipple:B: Indicates that the rectangle should be filled in a stipple pattern;Bspecifies the stipple pattern to use. If thefilloption hasn't been specified then this option has no effect. IfBisnilthen filling is done in a solid fashion.tags:Tag: Specifies a tag to apply to the item.width:I: Specifies the width of the outline of the rectangle. Wide outlines are drawn centered on the rectanglar path defined byX1,Y1,X2, andY2. If this option isn't specified then it defaults to 1.0.
TEXT ITEMS
A text item displays a string of characters on the screen in one or more lines. Text items support indexing and selection, along with the following tag methods: dchars, focus, icursor, index, insert, select. Text items are created with widget commands of the following form:
create(text X Y param1:value1 ... paramX:valueX) The arguments X and Y specify the coordinates of a point used to position the text on the display (see the options below for more information on how text is displayed). After the coordinates there may be any number of paremeters. The following parameters are supported for text items:
anchor:A: Specifies how to position the text relative to the positioning point for the item.Amust be one of the following atoms:center,n,ne,e,se,s,sw,wornw. This option defaults tocenter.fill:C: Specifies a color to fill the text characters.Cmust be a valid color (see Section 8.2).font:F: Specifies the font to use for the text item.Fmust be a valid font (see Section 8.8)justify:A: Specifies how to justify the text within its bounding region.Amust be one of the these atoms:left,rightorcenter. This option will only matter if the text is displayed as multiple lines. If the option is omitted, it defaults toleft.stipple:B: Indicates that the text should be drawed in a stippled pattern;Bspecifies the stipple pattern to use. IfBisnilthen filling is done in a solid fashion.tags:Tag: Specifies a tag to apply to the item.text:VS: Specifies the characters to be displayed in the text item. Newline characters cause line breaks.VSmust be an empty string.width:I: Specifies a maximum line length for the text. If this option is zero (the default) the text is broken into lines only at newline characters. However, if this option is non-zero then any line that would be longer thanIis broken just before a space character to make the line shorter thanI; the space character is treated as if it were a newline character.
WINDOW ITEMS
Items of type window cause a particular window to be displayed at a given position on the canvas. Window items are created with widget commands of the following form:
create(window X Y window:Desc param1:value1 ... paramX:valueX) The arguments X and Y specify the coordinates of a point used to position the window on the display. The Desc parameter is a usual description of a window (like td(...)) that is to display. After these parameters there may be any number of parameters. The following options are supported for window items:
anchor:A: Specifies how to position the window relative to the positioning point for the item.Amust be one of the following atoms:center,n,ne,e,se,s,sw,wornw. This option defaults tocenter.height:P: Specifies the height to assign to the item's window. If this option isn't specified, or if it is specified asnil, then the window is given whatever height it requests internally.Pmust be a valid screen distance (see Section 8.6).tags:Tag: Specifies a tag to apply to the item.width:P: Specifies the width to assign to the item's window. If this option isn't specified, or if it is specified asnil, then the window is given whatever width it requests internally.Pmust be a valid screen distance (see Section 8.6).
Note: due to restrictions in the ways that windows are managed, it is not possible to draw other graphical items (such as lines and images) on top of window items. A window item always obscures any graphics that overlap it, regardless of their order in the display list.